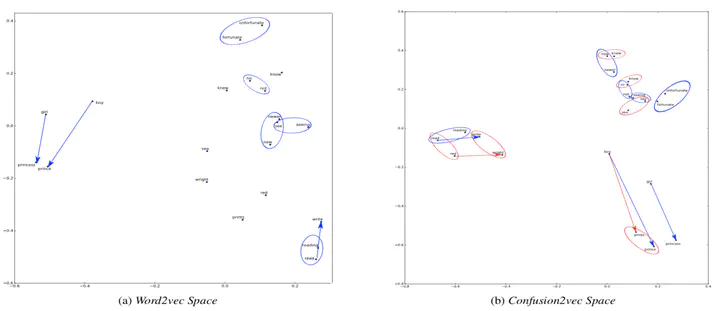
 Vector Space Comparision
Vector Space Comparision
Abstract
Decoding speaker’s intent is a crucial part of spoken language understanding (SLU). The presence of noise or errors in the text transcriptions, in real life scenarios make the task more challenging. In this paper, we address the spoken language intent detection under noisy conditions imposed by automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. We propose to employ confusion2vec word feature representation to compensate for the errors made by ASR and to increase the robustness of the SLU system. The confusion2vec, motivated from human speech production and perception, models acoustic relationships between words in addition to the semantic and syntactic relations of words in human language. We hypothesize that ASR often makes errors relating to acoustically similar words, and the confusion2vec with inherent model of acoustic relationships between words is able to compensate for the errors. We demonstrate through experiments on the ATIS benchmark dataset, the robustness of the proposed model to achieve state-of-the-art results under noisy ASR conditions. Our system reduces classification error rate (CER) by 20.84% and improves robustness by 37.48% (lower CER degradation) relative to the previous stateof-the-art going from clean to noisy transcripts. Improvements are also demonstrated when training the intent detection models on noisy transcripts.